EARTH'S SHAPE, MERIDIANS, PARALELS AND SEASONS

INTRODUCTION
In this day and age we know that the Earth isn't flat, but did you know that it neither is completely round? Besides, how do we do to organise it? The nature organises the Earth creating the seasons, but did the humanity invent any way to organise it? Of course we did. Those and many more things are what you are going to explore in this website.
HISTORICAL BASES

HIPPARCHUS OF NICEA

Hipparchus of Nicaea was a Greek astronomer, geographer and mathematician who was born in Nicea, in Turkey in the 19th century BC and died in 120 BC.
In geography he was the first to divide the Earth into meridians and parallels, making the concepts of longitude and latitude of a place or space usual, and he tried to faithfully project the spherical Earth into a two-dimensional map.
On the other hand, Hipparchus is the inventor of trigonometry, whose purpose is to relate the angular and linear measurements. The needs of this type of calculations are very frequent in Astronomy.

THE CONDAMINE
The first scientific expeditions of the century were those arising from the debate on the exact form of the earth globe, that is to say, the length of a meridian arc of one degree. These confirmed that the earth was flattened by poles.

This double expedition was organized in 1735 by the Academie des Sciences, who set the front of the trip to the polar regions to mathematicians Pierre Louis Moreau de Maupertuis and Alexis Clairaut, counting as an associate with Anders Celsius, who was able to observe and study the disturbances produced by polar auroras.
In addition, the directors of the trip were Charles Marie de La Condamine, known as "the soul of that French expedition," and Pierre Bouguer, founder of photometry.

ANAXIMANDRE

Anaximandre performed a measurement of the solstices and equinoxes by means of a gnomon, that is, a sort of sundial that he invented.
He also built a map of the Earth and a letter from the heavens. This was a circular map of Europe and Asia, only known regions, surrounded by the ocean. He affirmed that the Earth was cylindrical and that it occupied the center of the Universe. He carried out work to determine the distance and size of the stars.
Solstices and equinoxes are the four main points that determine the four stations in the Earth's orbit in its turn around the Sun:
ACTUAL KNOWLEDGE

THE SHAPE OF THE EARTH
First of all, the Earth is not flat. But the truth is that neether is completely round. Scientists use the term "geoid" to describe the shape of the planet, because it does simplify the matemathical matter and it is similar to the real shape. But the very truth is that we can't describe the shape of the Earth with a techincal word. Some people like calling it a "potato form", because it is as irregular as a potato.
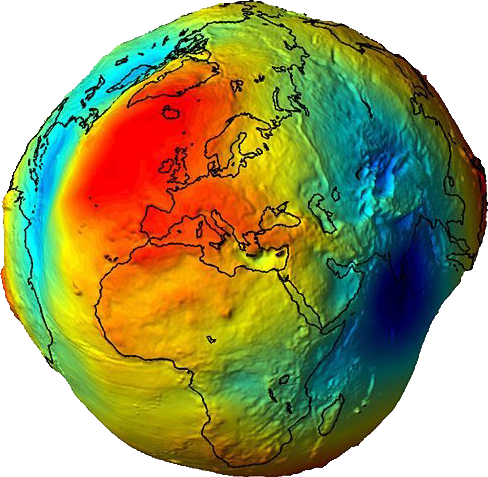
1. The Earth as a Geoid. Exaggerated picture.
The image 1 is made by the European Space Agency with the help of the sounding line Steady-State Ocean Circulation Explorer (GOCE). The heights are exaggerated but this makes really visual that irregularity of the surface.
In spite of the irregularities, when we take a real picture (such as the image 2) we can't really notice the diferencies. The planet is also fulfilled of gases and water that make the irregularities imperceptible from such a large distance.

2. Real picture taken by NASA.
There are some interesting factors that alter the shape of the planet. For example, it is flattened by the zones of the poles and wider by the Ecuador. This is becasue of the "centrifugal force"* that makes the rotation movement. The further from the axis of rotation, the more powerful is this force, making the further surface to be even more far, and compriming the poles (check image 3).
The sea neither is at the same height in the whole planet. It depends on the zone, because the temperature and water quality is different and that makes the density to vary.

3. The Earth is flattened by the poles.

PARALLELS AND MERIDIANS
The parallels are horizontal imaginary lines that have an east-west orentation. They are perpendicular to the earth's axis and decrease in size as you approach the poles.

The line of the equator is known as parallel 0°, which divides our planet into two equal halves:
- The North emisphere
- The South emisphere

The parallels are organized from 0° in the equator up to 90° at the North Pole and at the South Pole. The parallels allow us to define the latitude of a point at the earth, it's means, their position at Norh or at South of the parallel from equator (parallel chosen as reference).
Therefore, the latitude of a point can be defined as the distance between the parallel of a place and the equador, taken as the origin.
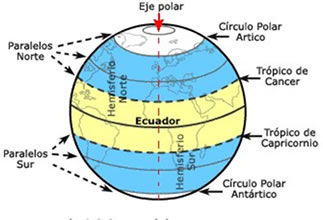
The meridians are vertical imaginary lines (or circles) that go from the North Pole to the South Pole. Each Meridian, with their respective antimeridian forms a cricle.

The reference Meridian is the Meridian 0 °, or Greenwich mean time; their antimeridian is 180 °.
- Both meridians form a circle that divides the Earth into Western hemisphere and Eastern hemisphere.
- Meridians are numbered from 0° to 180°, eastward and westward, completing 360° in total.
The meridians indicate the length, which is the distance measured in degrees from any point on Earth East or West of the 0 ° Meridian.

THE SEASONS
TRADITIONAL ASIAN / IRISH METHOD
The traditional astronomical method there is a lag with the data of the temperature the autumn here is warmer than the spring.
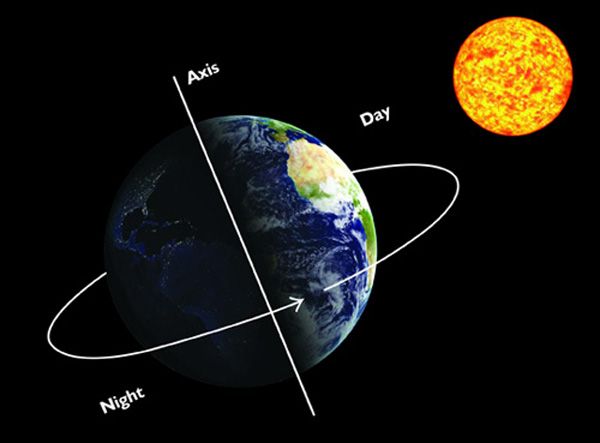
The seasons are due to the inclination of the axis of rotation of the Earth with respect to the plane of its orbit with respect to the Sun
In the equatorial regions of the Earth, the seasons are only two: the dry season and the rainy season; the rainfall regime varies, but the temperature does not vary much
THE CAUSE OF THE SEASONS
The axis of the Earth has an inclination of 23.45º, the consequence is that the Sun, in its route along the ecliptic during a year

The inclination of the Earth's axis is responsible for changes in the height of the Sun over the horizon and the succession of climatic situations that give rise to the seasons
SEASONAL CLIMATE CHANGES
One of the main reasons why the temperature varies so much in the temperate zones throughout the seasons, is how the energy coming from the Sun can effectively heat the Earth's surface
This means that during the winter receives less than half of the energy it receives during the summer, which is why the environment is colder.
HOW ARE THE SEASONS ON OTHER PLANETS?
The passage of the seasons, especially in the temperate regions of the Earth, implies the alternation of a series of climatic and meteorological changes that are part of the life cycle of many ecosystems on our planet.
VIDEOS

Some videos of interest.
This is a video we've made in order to explain some experiments you can try to demonstrate that the shape of the Earth is round.
This is a spanish parody. This three guys made a song about the terraplanism and the people who believe in it. It is not only fun, but also makes fun of some arguments that terraplanists use and mention some scientific concepts.
This is a short video that explains the difference between Paralels and meridians graphically.
ABOUT US

Last but not least

Ángel Lapeña López
Marketing departament and actual knowledge.
Winner of diverse awards such as the Academic Excelence in primary and secondary, actually studying scientific-technological A levels in Florida Secundària. My hobbies are editing videos, creating animations and playing videogames, and my dream is to be an important physicist.

Andrea Mena Jorge
Actual knowledge
Winner of one literature award, actually studying scientific-technological A levels in Florida Secundària. My hobbies are, listening music, dancing and traveling. In the future I would like to study biomedic-engineering, and be a good engineer.

Kayla Marie Wainsztein Di Vito
Media department, actual knowledge and mixed group
Student of A-Levels in STEM in Florida Secundària and aspiring mechatronics engineer. I enjoy activism, editing and creating videos and collages, and robotics. My dream is to make ethical and sustainable technology.

Nerea Tordera Rodríguez
Research department and historical bases
I´m 17 years old,I live in Picanya
Actually studying scientific-technological A levels in Florida Secundària
My hobbies are travel to other countries, listen to music,walk on the beach
In the future I will like to be a teacher of children of infant education

Marcos Magalló Beamud
Research department and historical bases.
Good worker, cooperative and very tidy. Actually studying scientific-technological A levels in Florida Secundària. My hobbies are playing videogames and driving karts. In the future I will like to be a mechanical engineer of Formula 1 or MotoGP.
