DISTANCE TO THE SUN, PLANETS AND THE REST OF THE STARS


FRED HOYLE: was a British astronomer known mainly for his theory of stellar nucleosynthesis and his often controversial positions on other cosmological and scientific issues, especially his rejection of the "Big Bang" theory, a term he coined in a radio program of the BBC .

.
EDMON HALLEY: was an English astronomer, mathematician and physicist, known for calculating the orbit of Halley's comet. He was a friend of Isaac Newton and a member of the Royal Society.

PRESENTATION TEXT
In this part of the web we are going to talk about a few astronomical distances.
The investigation of the distance from the earth to the sun, began between 310-230 a.C.
Within this theme we find:
EDWIN HUBBLE: was one of the most important American astronomers of the 20th century, famous mainly for the general belief that in 1929 he had demonstrated the expansion of the universe by measuring the redshift of distant galaxies. Hubble is considered the father of observational cosmology although his influence in astronomy and astrophysics touches many other fields.

FRANK DRAKE: is an American astronomer. He has participated and directed numerous projects to search for extraterrestrial life since he himself carried out the first of all, the Ozma project in 1960.


HISTORICAL BASES

SUN:
The astronomical unit that accurately measures the distance between the Sun and planet Earth and equals exactly 149 597 870 700 m.
In this way, scientists can quantify distances in space using this unit and facilitate their work.
The distance between the two celestial bodies could be measured using modern technology that allowed to do so accurately. Thus they have established a unit that determined the distance makes an average of, because the Earth, by orbiting the Sun following the Kepler model with an elliptical trajectory, there are moments in which it is more or less distant from the Sun . About January 4, the Earth is as close as possible (Perihelion): about 147 million kilometers away from the Sun. On the other hand, it is around the 4th of July the time of greatest distance (Afelio), when it increases to 152 million kilometers.

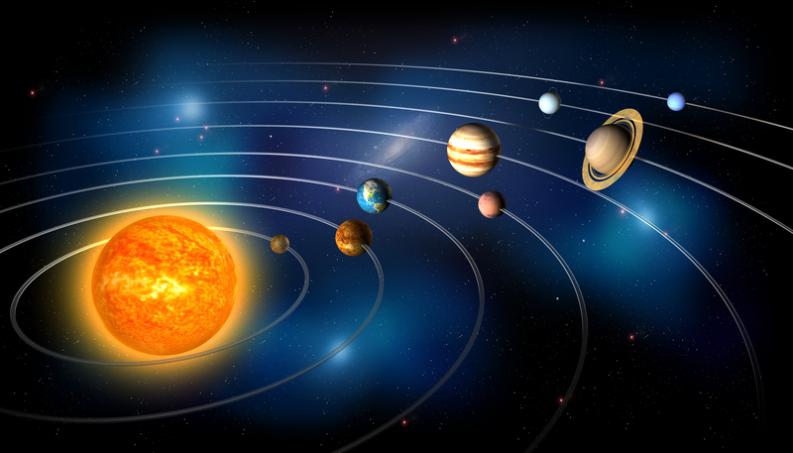
The distances are as follows:
Earth-Mercury: 101000000 km (0.68 AU)
Earth-Venus: 40000000 km (0.27 AU)
Earth-Mars: 58,000 milions (0.39 AU)
Earth-Jupiter: 59,400,000,000 Km (3.98 AU)
Earth-Saturn: 1207000000 km (8.08 AU)
Earth -Uranium: 2601000000 km (17.4 AU)
Earth -Neptune: 430,600,000,000 Km (28,8 UA)
PLANETS:
The distance of the planets from the Sun is measured in Astronomical Units (AU) at two different orbital moments: the perihelion and the aphelion. Perihelion is the distance of a planet from the sun measured at its closest orbital point; and the aphelion at its farthest orbital point.
To calculate the distance between the planets we must imagine for a moment that they are perfectly aligned and they are all in the same orbital period.
This, of course, is not at all accurate: the planets are not aligned and their orbits are not all equal to each other. But to have an idea of what the distance between them is, we need to imagine that hypothetical scenario.
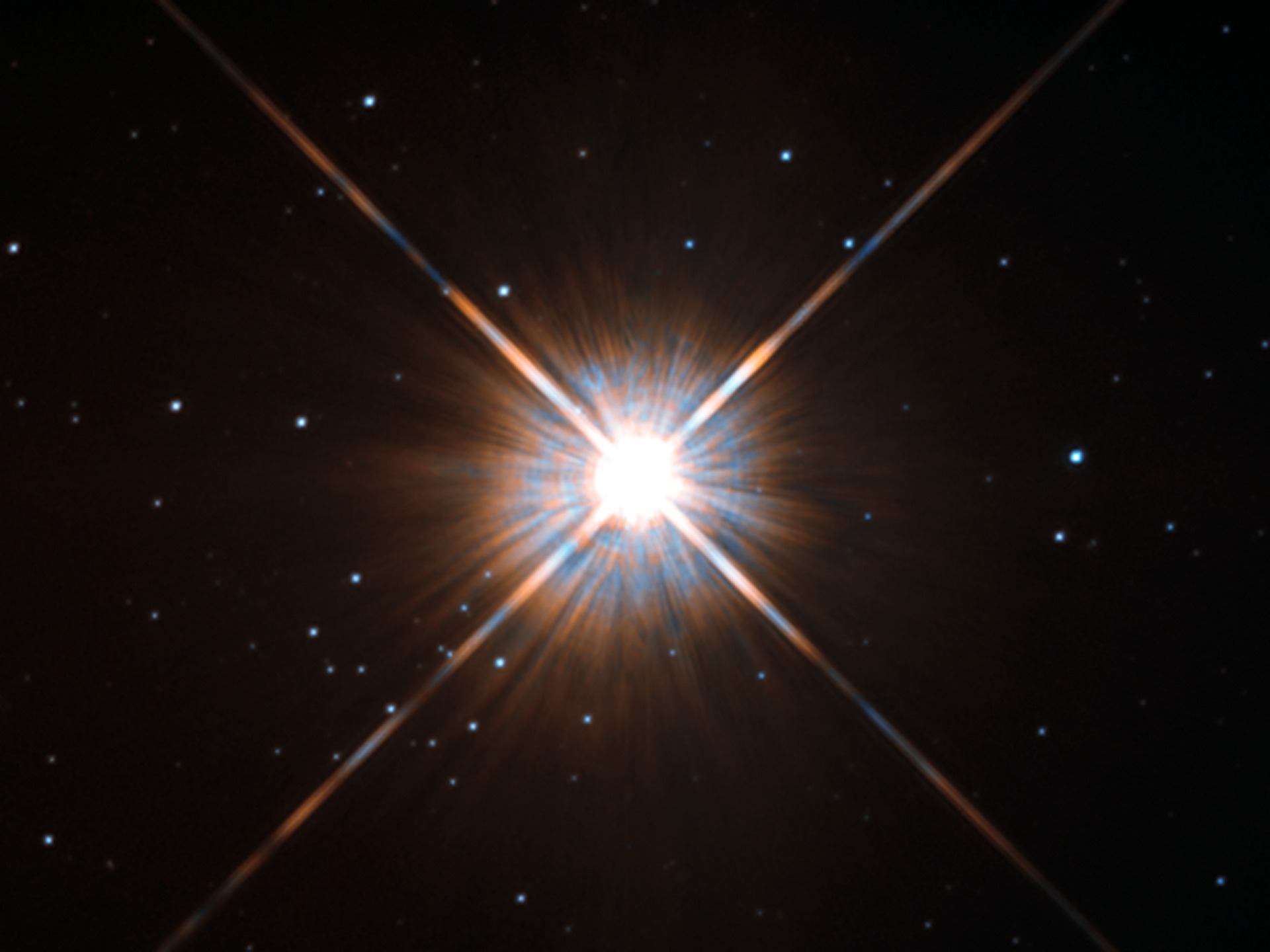


Farther stars appear weaker because their light spreads and then diffuses. So if you know how bright the star should be and compared to how bright it really is, we should be able to know how far it is.
Very distant stars
To measure distances to stars outside the Milky Way, astronomers depend on exploding stars.
Supernovae have several shapes and sizes, but one especially "supernova type" is especially important to measure the cosmos. Explosions occur in binary systems, in which a white dwarf begins to absorb its companion, a red dwarf. As the mass of the white dwarf begins to increase an uncontrolled fusion reaction occurs causing it to explode into a thousand pieces.
There is a very specific size limit where this happens, so all supernovas of this type have approximately the same mass, which means they have the same brightness. If we can compare the mass with its relative brightness we can know how far it is.
STARS:
In the same way that we use a ruler to measure a few centimeters or a tape measure to measure several meters, astronomers use different tools according to the scale of measurement. The set of methods is called the cosmic distance staircase, in which each method provides information that can be used in the next step, always using the physics of light.
Nearby stars
The distance to the nearby stars of the Milky Way is measured with simple trigonometry, as the Earth moves around the Sun the position of the star in the sky seems to change in relation to the more distant stars, this is called parallax.
This only works with relatively close stars, for distant stars the parallax vision is extremely small. To measure the distance to farther stars we will have to use other properties of light.
Distant stars
Variable stars are stars that change brightness in a period of time ranging from a few hours to a few weeks, due to the expansion and cooling of the helium with which they are formed. There is a relationship between the brightness of the star and its period. These stars are called Cepheid variables and their discovery allowed the cosmology to advance to its present point.
THE TEN MORE NEARBY STARS
- Próxima Centauri Distance: 4.2 AL - Luyten 726-8A and B Distance: 8.73 AL
- Rigel Kentaurus Distance: 4.3 AL - Sirius A and B Distance: 8.6 AL
- Barnard Star Distance: 5.9 AL - Ross 154 Distance: 9,693 AL
- Wolf 359 Distance: 7.7 AL - Ross 248 Distance: 10.32 AL
- Lalande 21185 Distance: 8.26 AL - Epsilon Eridani Distance: 10.5 AL

CURRENT KNOWLEDGE
There are 52 stellar systems beyond our own Solar system that currently lie within 5.0 parsecs (16.3 light-years) of the Sun. These systems contain a total of 63 stars, of which 50 are red dwarfs, by far the most common type of star in the Milky Way. Much more massive stars, such as our own, make up the remaining 13. In addition to these "true" stars, there are 11 brown dwarfs (objects not quite massive enough to fuse hydrogen), and 4 white dwarfs (extremely dense objects that remain after stars such as our Sun exhaust all fusable hydrogen in their core and slowly shed their outer layers while only the collapsed core remains). Despite the relative proximity of these objects to Earth, only nine (not including the Sun) are brighter than 6.5 apparent magnitude, the dimmest magnitude visible to the naked eye from Earth

In September of 2012, it was confirmed that the distance between the Sun and our planet is 149,597,870,700 meters, neither more nor less. The astronomers established the exact distance in the last International Astronomical Union. Thus this distance, a very important measure to perform astronomical calculations, is no longer the result of a complicated equation and becomes a concrete figure. This novelty will not change the world, but it will facilitate the work of astronomers and allow them to make their calculations more accurately.
The distance between the Earth and the Sun, called "astronomical unit" (UA), serves astronomers as a unit of measurement for calculating orbits and trajectories within our Solar System and in other star systems and distances between stars of binary systems.

EXPERIMENT

TEAM

CARLOS SORIA
I am 16 years old and I am from Valencia.
As you can see in my picture, I love nature and go for a walk.
I am very interested in knowing how the LHC works, really understanding what the particles are and why these minorganisms have been the creators of the whole.
DANI VIUDES
I' m 16 years old. I like do sports and meet friends the weekends.
What interests me is why was creation an explosion and when ends the universe.

ANTONI BALDÓ
I'm 16 .
I live in the Port, on the outskirts of Valencia and I love sports, specifically basketball, although I play Waterpolo.
In my free time i like to investigate things about the universe and what i like most abouit it is knowing wher we came from or how everything originated

